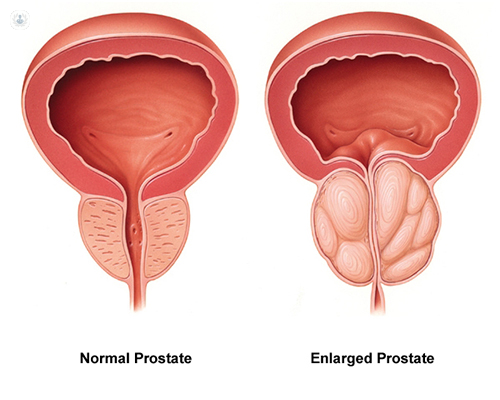
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy, or BPH, is a common problem in older men, and occurs as the prostate enlarges over time.
The prostate is a gland that sits below the bladder and surrounds the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder). As it enlarges, it can press on the urethra and makes it more difficult for patients to urinate.
Symptoms:
- Slow stream
- Getting up at night time
- Needing to urinate frequently or urgently
- Leakage of urine
- Not feeling as though the bladder is empty after urinating
- Blood in the urine
- Urinary tract infections
- Not being able to urinate at all
Diagnosis of BPH may include some or all of the following tests:
- History
- Physical exam, including a rectal exam to feel the prostate
- Urine tests
- Blood tests
- Urine flow test
- Ultrasound of kidneys and bladder
- Cystoscopy
Treatment depends on the severity of your symptoms, and how bothered you are by your symptoms.
Options include:
- Healthy bladder habits
- Medicine
- Surgery
Lifestyle modifications:
- Limiting fluid intake before bedtime
- Avoiding bladder irritants (coffee, tea, alcohol, spicy food, citrus food)
- Avoid constipation
- Weight loss
- Smoking cessation
- Timed voiding
Medication options:
- When medical therapy is considered, the first-line treatment is typically an alpha-blocker
- These medications work immediately
- Alpha-blockers relax the muscle cells in the bladder neck and the prostate
- Allow the urine to flow faster and the bladder to empty better
- Common options include: Tamsulosin, Terazosin, Silodosin, and Alfuzosin
- Side effects: dizziness, low blood pressure
- In patients with an enlarged prostate, a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor might be considered
- This medication shrinks the prostate size by 30%, so is most helpful in men with larger prostates
- This medication takes about 6 months to come to full effect
- It will also decrease your PSA by about 50%
- Common options include: finasteride or dutasteride
- Side effects: sexual side effects such as decreased libido, or worsening erections are seen in about 5% of men
- In men with severe symptoms, your doctor may consider using these 2 medications together to try and manage the symptoms
Surgical options:
- Surgery is an option for men with bothersome urinary symptoms caused by their prostate
- Indications for surgical treatment include:
- Bothersome symptoms
- Urinary retention, or the inability to void
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Recurrent gross hematuria (visible blood in the urine)
- Bladder stones
- Kidney failure secondary to prostate obstruction
- The most common surgical option in the Comox Valley is the Greenlight laser photovapourization of the prostate
More information:
Mayo Clinic: Click Here
